Are you curious about the science of refrigeration? Then stay tuned, this blog will offer you a simplified overview of the Refrigeration Function. Moreover, you’ll gain precise & concise knowledge of the Refrigeration Process (How it Works, Step-by Step Process, Key Components,). In brief, Refrigeration is a process that involves the removal of heat from an enclosed space using a cooling agent.
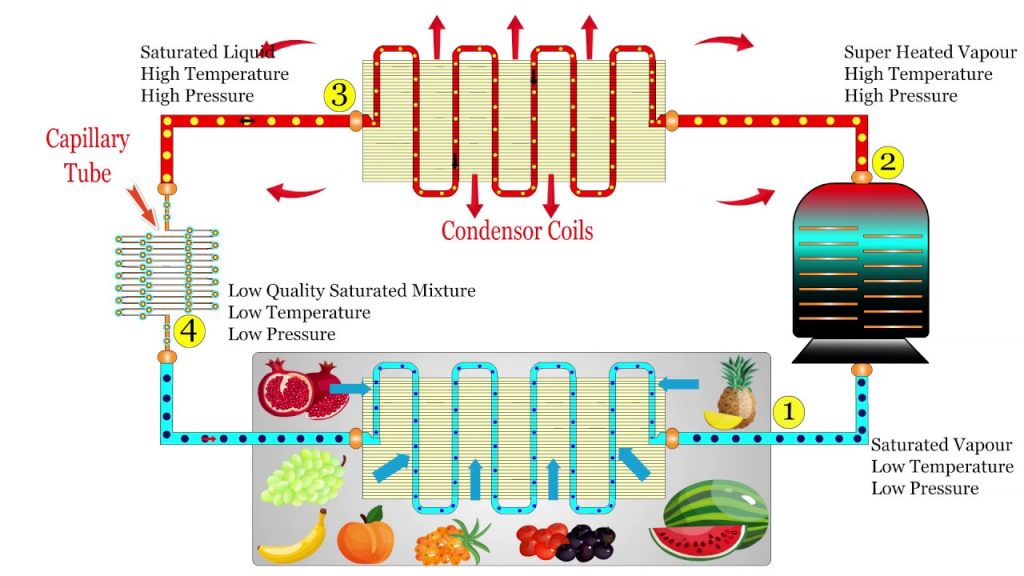
Refrigerator Functions by removing heat from the food and transferring it into the surroundings via a coolant. Then the compressor compresses & heats up the coolant. Once compressed, the coolant passes through the condenser coils at the back of the refrigerator, where it dissipates its heat.


When the coolant passes through the expansion valve, it expands and becomes a cold gas. The cold gas then passes through the expansion coils within the fridge, absorbing heat from the food items and preserving them.
Perhaps, Refrigeration Function serves a vital role in our lives, helping to keep food fresh and cool. With the process of Refrigeration, you can keep your food & beverages cold, which extends the shelf life of your food & beverages.
Refrigeration Function: How does it work?
At the most basic level, Refrigeration works by using a refrigerant, such as Ammonia or Freon, to absorb heat from an enclosed space. Then the refrigerator compresses the liquid and moves it towards a condenser coil outside the enclosed space. After that the Condenser Coil converts & cools the refrigerant into its liquid form, and the heat gets released outside.
Then the cooled liquid moves back to the evaporator coil inside the enclosed space, where the evaporator coil performs evaporation & heat absorption. The process keeps repeating in a cyclical manner over and over again, allowing the enclosed space to remain cool.
Refrigeration Function involves thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, and heat transfer principles. It involves understanding the properties of different refrigerants and how they interact with other materials. It also requires a knowledge of the techniques and equipment used to install and maintain refrigeration systems.

In fact Refrigeration System plays a prominent role in Air Conditioning & Modern Cooling Systems. With further technological advancements, refrigeration systems are becoming more efficient and eco-friendly.
Refrigeration is a vital technology for many industries, including food service, health care, and manufacturing. Whether you’re an engineer, technician, or just a curious individual, understanding the science of refrigeration can help you appreciate the technology we use every day.
Check out our blog to learn about the Science of Air Conditioning
Refrigeration Function: Step by Step Process
- During the compressor’s compression process, the refrigerant gas is heated up as it is pressurized.
- As fast as the hot refrigerant gas can dissipate its heat through the coils on the back of the refrigerator, it begins to condense into liquid under high pressure.
- As liquid flows through the expansion valve, it is under high pressure.
- Upon boiling, the liquid vaporizes and its temperature drops to about -25°F. As the cold gas flows through the expansion coils (inside the refrigerator), it absorbs heat and makes the inside cool.
- The compressor sucks up the low-pressure refrigerant gas and repeats the cycle.
Parts involved in the process of Refrigeration Function
1. Compressor:
A refrigerator’s “heart” is the compressor, which circulates refrigerant throughout the system and adds pressure to a warm part of the circuit, which heats it, in a similar fashion to when you press air into a bicycle tube – as you compress the air, the pump feels hot.
2. Condenser:
Typically, the condenser is located on the back of a refrigerator and it is likely that they are dusty. Condenser performs refrigerant cooling & refrigerant transformation into liquid state.
3. Evaporator:
A refrigerator’s evaporator keeps the food in the refrigerator cold as it transforms refrigerant from a liquid into a gas through evaporation. After this process, the area around the evaporator is cooled, maintaining a suitable environment for food storage.
4. Capillary Tube:
Capillary tubes serve as expansion devices, allowing the liquid refrigerant to flow through them and into the low-pressure environment of the evaporator. It is a thin tube used as an expansion device, which allows liquid refrigerants to flow into the low-pressure environment of the evaporator.
5. Thermostat:
A thermostat controls cooling by monitoring the temperature and turning on and off the compressor. When the sensor senses that the refrigerator is too cold, it turns off the compressor. When it senses too much heat, it turns on the compressor and starts cooling.
Conclusion
Refrigeration is a key component to keeping food safe and enjoyable. It is important to maintain the refrigerator regularly to ensure it is running properly and efficiently. Regular Refrigeration Servicing can help you enhance the Refrigeration Function. It’ll extend the shelf life of the refrigerator, while ensuring that your food stays fresh.



